The outer ear collects sound waves and directs them into the ear.

Hearing health is freedom!
Our network of providers will ensure you receive the professionalism and superior care that you seek and deserve.
Learn moreA Major Link to Wellness
The ability to socialize. The desire to venture out of the house. Improved work productivity – all these scenarios are affected by our capacity to hear well.

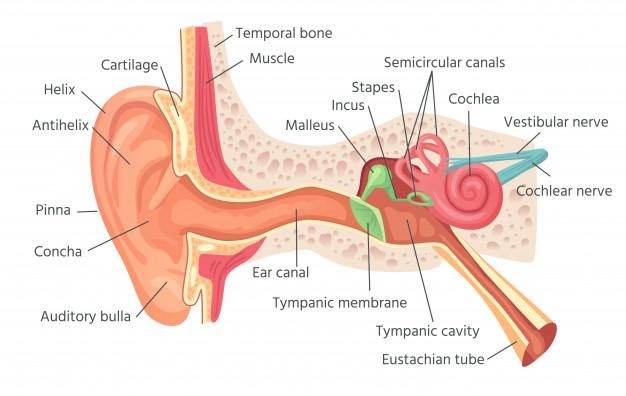
Anatomy of the Ear
The ear detects and analyzes sound by transduction, maintains equilibrium, and is made up of three parts – the outer, middle and inner ear.
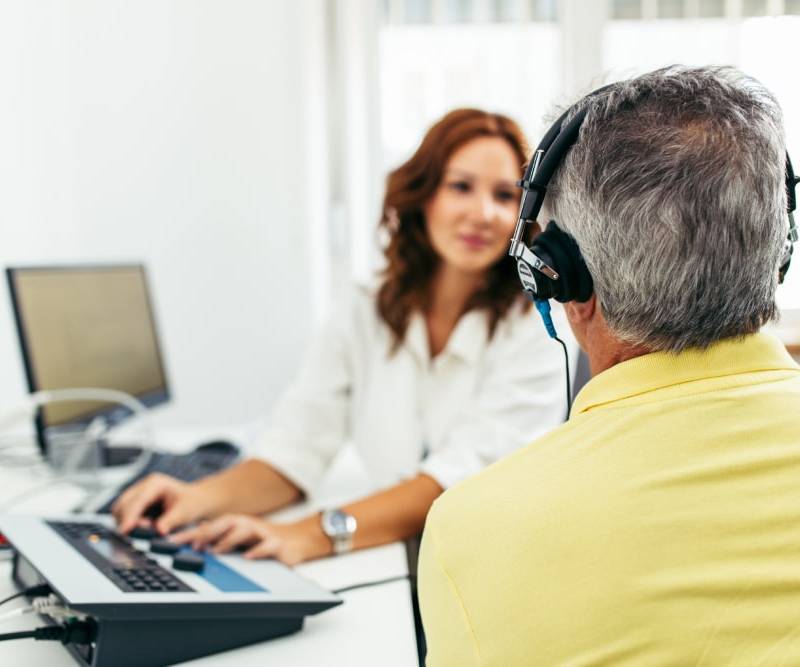
Hearing health begins with check-ups.
Untreated hearing loss can go undiagnosed for years, and usually you are the last to know.
The first step to maintaining healthy hearing is to schedule a hearing exam. The general rule of thumb is that you should have your ears tested every three years. If you work in a noisy environment, you should have your ears checked more often. People over 50 should have yearly ear exams.
Knowing where your hearing stands provides the benefit of providing a baseline that can help your doctor to detect any hearing issues in the future.

Prevention Best Practices
While regular hearing exams is one prevention technique, there are other practices that you can begin that will help to preserve your hearing health.
Avoid loud activities and places.
Use earplugs or noise reduction headphones.
Try to move away from the loudest sound source (e.g. speakers).
Turn down the volume on your TV, music, mobile phone, etc.
Avoid using cotton swabs, other small items to scratch or clean your ears.
Exercise to improve blood flow and avoid high levels of stress.
Manage your blood pressure and cardiac health.
Limit alcohol consumption and say no to smoking and vaping.
If you’re diabetic, manage your sugar levels.
Incorporate B12, potassium, iron and magnesium into your vitamin supplement regimen or eat foods rich in these vitamins and minerals.

Types of hearing devices:
Should you experience significant hearing loss, an audiologist may suggest the use of a hearing device. There are several types of hearing aids and implants. Some perform different functions.
Hearing Implants
Should you require a hearing aid, seek the advice of your audiologist, ask for a trial period to ensure the device is right for you, and check for a warranty.